Low Back Pain
Contents
Overview
The lumbar spine, also known as the lower back, is an intricate structure of interlinked bones, ligaments, nerves, joints, and muscles all working synergistically to provide flexibility, strength, and support.
Its unique structure, however, makes it very vulnerable and susceptible to injury and pain.
To better understand the complexity of spinal health, we will be presenting a guideline for understanding symptoms, injection techniques and physical findings to come to an accurate diagnosis.
After attaining an accurate diagnosis of the cause of your lower back pain, a course of treatment will be set based on the latest and best medical practices.
Types of Back Pain
Back pain can be categorised in many ways but the two most common types are:
Mechanical pain
This is a common cause of low back pain. Also known as axial pain, it originates from ligaments, muscles, joints or bones in and around the spine.
This pain is mainly localised around the upper thigh, buttocks and lower back. This pain is caused by loading the spine and can feel different depending on activity, movement, sitting, standing or resting.
Radicular pain
This type of pain occurs when a spinal nerve root is inflamed or impinged. Radicular pain can follow a nerve root pattern or dermatome into the buttocks or upper thigh. It is characterised by an electric, sharp and burning pain. This pain can cause sciatica, weakness or numbness on one side of the body.
The lower back consists of discs that have spinal nerves channelling form either side. Low back pain can cause nerve compression or irritation leading to knee pain. The nerve irritation or compression or injury to lower back muscles which link to the hip can also lead to chronic back and severe hip pain.
Typical Symptoms of Low Back Pain
Low back pain can include a wide range of symptoms. Some symptoms can be mild and annoying or severe and debilitating. It can also start suddenly or progress slowly getting worse over time.
Symptoms can vary depending on the primary cause of the pain. Symptoms can be experienced as:
A dull or achy pain originating from the low back
A burning or stinging pain that spreads from the low back to the back of the thighs or feet
Muscle tightness or spasms in the pelvis, hips or low back
Pain that worsens after prolonged standing or sitting
Difficulty walking, standing upright or switching from standing to sitting
Onset and Duration of Low Back Pain
Symptoms can also be described by duration and onset. The time frame of how the pain occurred can give us clues as to how severe the injury is, and potential causes. This includes:
Acute pain: This type of pain normally starts unexpectedly and can continue over a few days or weeks. This is considered to be the body’s involuntary response to injury or tissue damage. This pain can progressively subside as the body heals.
Sub-acute low back pain: This type of pain normally is mechanical in nature and can last between six weeks and three months. If the pain is severe and limiting to an individual’s ability to carry out normal daily activities it can be wise to seek medical intervention.
Chronic back pain: Lower back chronic pain is characterised by low back severe pain that over three months. The pain is severe and it does not respond to initial treatment. A thorough workup can be done to establish the precise source of the pain.
Why Lower Back Pain May Be Worse in The Morning
Lower back pain first thing in the morning can happen for a variety of reasons. Unfortunately, pain in the morning does not tell us precisely what is causing your back pain. Nonetheless, here are a few reasons why your back pain may be worse in the morning:
Osteoarthritis: or ‘wear and tear’ arthritis, typically presents as 30 minutes of low back stiffness first thing in the morning that improves as you start to get moving
Poor sleeping position: often results in low back pain when people lay twisted. A good way to resolve this is to sleep with a pillow between your knees if you sleep on your side. If you sleep on your back, then place a pillow under your knees.
Stiffness caused by swollen discs: when irritated, discs in the lumbar spine can become swollen overnight. This is due to the fact that healthy discs typically respond well to compression (ie. When we sit or walk around during the day). However, when we sleep at night, the discs are not under any pressure and thus become swollen. This may create some discomfort but typically improves as you start moving.
Injury or lack of movement: patients often complain of low back pain/stiffness if they have been lying in bed for longer than usual. This can happen if they’re sick with the flu, or even trying to rest for another injury. Muscles and joints in the low back need movement on a regular basis. If they don’t move for a while, they begin to stiffen up. So if you’ve had an extra-long sleep, you might wake up a bit stiff!
Causes of Low Back Pain
Over 80% of the population will suffer from low back pain at some point in their life. An injury to the back causes the body to react by initiating an inflammatory response. This makes it easier to establish the cause and source of the pain since the overlapping intricate network of discs, ligaments, muscles and other spinal structures make it difficult for the brain to establish the cause. The pain duration can also help determine the cause of the pain.
Back pain can be caused by a number of problems commonly linked to joints, muscles, and ligaments especially when they are strained. Strains can be due to overworking the lower back area. However more serious issues occur when your nerves and spinal cords are injured through an accident or degeneration due to nerve and spinal diseases. Spinal ligament and muscle injuries can heal fast but a torn disc may not respond as quick.
Although most back pain episodes are triggered by muscle injury or overuse, it can also be the result of spinal conditions such as:
Lumbar herniated disc
Degenerative disc disease
Facet joint sprain/dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
The spinal conditions mentioned above can present in a variety of forms and thus is best to have this examined by a chiropractor before making a diagnosis. Other conditions that can cause low back pain include spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis, spinal tumours, piriformis syndrome, and fibromyalgia.
Low Back Pain Caused by Ligament Sprains and Muscle Strains
A low back sprain or strain can happen in two ways. It can either happen gradually over time from routine and repetitive movements, or occur suddenly, for instance, while lifting a heavy load.
Strains occur when a muscle is stretched over its limits causing it to tear thus damaging the muscle. Sprains develop when the stretching and tearing extend to the ligaments. Sprains and strains can be caused by poor sitting position over time, sudden movements that place stress on the spine, heavy lifting that may cause the spine to twist, and sports injuries.
Sprains and strains can sometimes cause severe pain even though they do not sound serious and are not long lasting.
Determining the exact cause of your low back pain can be difficult and requires a full workup. Nonetheless, here is a more detailed description of common causes of low back pain:
Lumbar Herniated Disc: A disc is a fibrocartilaginous joint that allows for the vertebrae in the spine to move while holding them together. Also known as slipped disc, it occurs when the soft jelly-like center of the spinal disc bulges out (herniates) through the harder outer casing via a tear and come into contact with a root nerve and cause irritation. This, in turn, causes chronic pain in the back.
Degenerative Disc Disease: As people age, their intervertebral discs lose hydration and wear out. As it loses hydration, it cannot act as the shock absorber it used to, therefore, transfers pressure to the disc wall. The pressure causes the wall to tear or weaken leading to herniation. Both situations cause pain to the lower back.
Facet Joint Sprain/Dysfunction: A facet joint are joints in the spine that make the back flexible enabling you to bend and twist your back. There are two facet joints connecting the disc at each motion point in the lumbar spine. The joints have cartilage surrounded by ligaments richly surrounded with nerves. By themselves, the joints can become painful due to wearing out or be painful in conjunction with disc pain.
Sacroiliac (SI) Joint Dysfunction: This joint connects the sacrum at the bottom of the spine on each side of the pelvis. Its purpose is to absorb tension and shock between the lower body and the upper body. Pain comes about by inflammation in the joint caused by sacroiliitis. It can also be caused when there is too much movement or less movement in the joint.
Risk Factors for Low Back Pain
Apart from the above-listed causes of acute and chronic back pains, there are lifestyle related causes that increase your chances of suffering from lower back pain. They include:
Fitness level where people who are not physically fit tend to develop back pain
A diet high in calories and fat combined with an inactive lifestyle may lead to obesity which leads to stress on the back.
For people who use hip flexors like athletes, if they are too tight, they tend to compress the lower back and cause injury. The compressions weaken your gluts causing your hamstrings and muscles to overwork hence the pain.
Treatment Options
Lower back pain that is not caused by serious injury or a condition or disease normally resolves after about four weeks of active recovery. However, if the pain does not improve after a number of days or worsens over time, then you need to have your back examined.
There are many treatment options for lower back pain, most of which are unique and tailored to fit the patient’s diagnosis. These treatments can be surgical or non-surgical. Some of these treatment options need to be administered by a professional such as a chiropractor, physiotherapist, or doctor while others can be done at home.
Here are some of the answers to the questions you may have about treatment, recovery, and prevention of lower back pain.
Does chiropractic work for lower back pain? Should I see a chiropractor for lower back pain?
Many people with lower back pain seek treatment that is non-surgical and non-medical as it bears the least amount of risk.
Chiropractic has particularly shown great results in patients with lumbar problems. Research shows that 22 million Americans visit chiropractors annually and at least 35% of them are suffering from back pain.
A chiropractor adjusts and corrects the spine using hands-on manipulation techniques coupled with various other alternative treatments. The concept behind chiropractic adjustments is that a spine that is moving well will help the body heal without the need for medication or surgery. This manual manipulation will help fix your posture, increase mobility, ease lower back pain, and even get rid of it completely.
At Perth Sports Chiropractor, we administer chiropractic adjustment treatment to our patients to help relieve your lower back pain and improve your body's mobility.
Every patient's treatment session is case specific and depends on the cause of your back pain. The speed and force of the hand movements manipulate different parts of the spine and are designed to continuously alleviate your condition starting from your first session.
Read more about Low Back Pain…
What are good exercises for lower back pain?
Although chiropractic treatment will give you relief from lower back pain, accompanying it with rehabilitation stretches and exercises will help speed up the healing process and ensure long-term positive results.
Walking and swimming are simple exercises that are safe and easy to do. It is beneficial in the early stages of low back pain to help loosen the muscles and reduce muscle spasm but unfortunately, this will not fully remove your low back pain. Stretches and individualised exercises are required to achieve a more permanent result.
At our clinic, we offer rehabilitation and exercise programs that helps patients recover from injuries as well as post-surgery. Our programs focus on restoring your daily function and furthering your performance to reduce back injuries or pain in the future.
How to Strengthen Lower Back Muscles after Injury
After an injury to the lower back muscles, it is important to incorporate an exercise program to strengthen the injured tissues. Depending on your injury, this can vary from exercises focusing in the lower back or alternatively, the core muscles in your stomach that support your spine.
Strengthening exercises that focus on your core muscles (abdominal, gluteus, and hip muscles) will help in back pain relief. These muscles support the vertebrae in your spine as well as your spinal cord. With the help of a sports chiropractor, you can learn specific exercises designed for your body to help alleviate and fix your condition.
WARNING! Crunches don’t help with back pain! Although sit ups and crunches are traditionally thought of as ‘core exercises’, they actually do very little for core strength and low back pain. On the other hand, exercises such as planks are much more effective at improving core strength and improving stability through the low back.
Here are a few videos of strengthening exercises for low back pain:
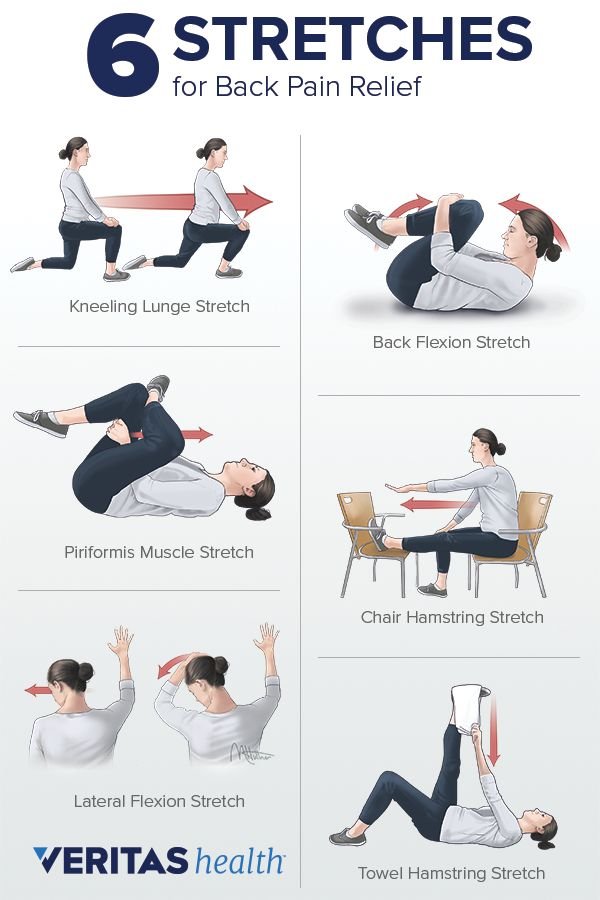
Stretches for Low Back Pain
Stretching is one of the simplest exercises that will help you relieve lower back pain at home. When you have a low back injury, the muscles in your lower back, legs, buttocks, and hips tend to spasm as a protective mechanism. Unfortunately, this is often an overreaction by the body and can contribute to pain. Below are some basic stretches you can do for low back pain. However, be aware that these stretches are not appropriate for ALL back injuries. In fact, they may make some injuries worse so it is important to speak to your chiropractor before trying out any of these stretches.
Also, before you begin any strenuous activity such as mowing the lawn or lifting heavy boxes, you should also do a few dynamic stretches to warm up your back and prevent any injury to your back.
At-Home Treatment
If you have back pain, here are some easy ways to alleviate the pain through self-care. It is important to pair these treatments with your chiropractic adjustments to achieve the best and fastest results:
Active recovery – keep yourself active by continuing with your normal daily activities. You may need to modify the duration of these activities but the worst thing you can do is lie around all day.
Try not to sit or lay around too long. Set a timer and force yourself to move every 20-30 minutes at the very least
Use hot packs. Heat increases blood flow and reduces muscle spasming, which helps with pain relief and muscle tension
Try to minimise your stress and anxiety levels, as this can contribute to further muscle guarding
Maintain a good posture when sitting, standing, and walking
Eat a healthy anti-inflammatory diet
Avoid high heels
How to Sleep with Low Back Pain
Sleeping in the right position will help to ease the pain in your lower back. The ideal position to sleep is on your back or on your side. However, it may be difficult to change your sleeping habits during an acute flare up of low back pain.
If you prefer sleeping on your back, keep your knees bent and place a pillow under your knees so your low back does not arch off the ground. If you’re a side sleeper, put a pillow between your legs and draw your knees slightly towards your chest. This will minimize the amount of twisting in your low back.